4. Docker Compose 서비스 만들기
1. 사용가능한 서버
- 특정 IP를 가진 서버(RTX2080TI 서버)를 통해야만 NIPA 서버에 접속할 수 있다.
- RTX2080TI 서버와 NIPA 서버 모두
9003번 포트가 열려 있다.
2. 서비스 아키텍처
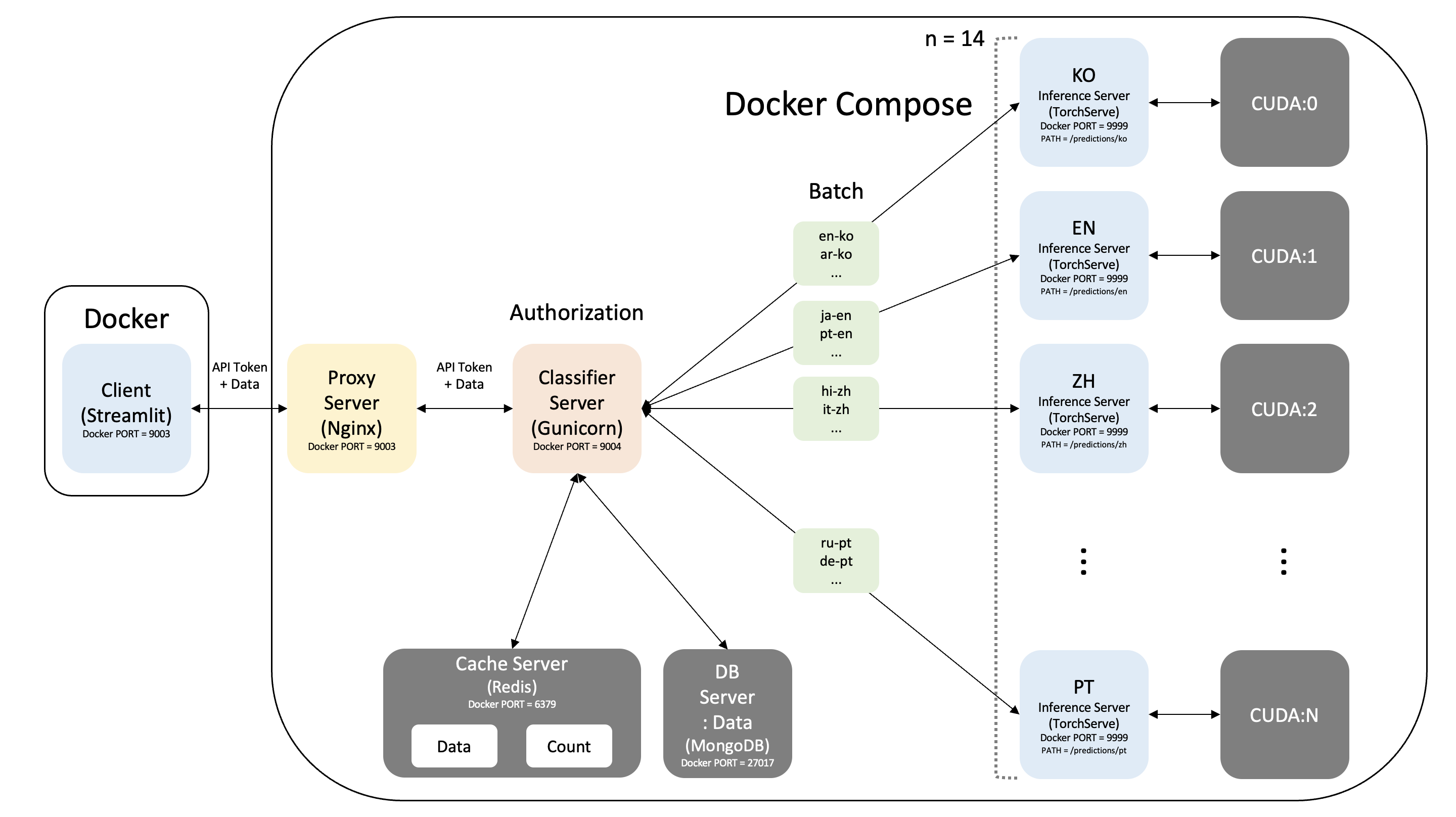
1) RTX2080TI 서버
- 클라이언트를 담당하는 서버
- Docker 환경
- Streamlit
2) NIPA 서버
- 서비스를 담당하는 서버
- Docker Compose 환경
1] Proxy Server
- Nginx
2] Classifier Server
- Gunicorn + Uvicorn + FastAPI
3] Inference Server
- TorchServe + Hugging Face + CUDA
4] Cache Server: Data / Count
- Redis
5] DB Server: Data
- MongoDB
3. 서버 기본 세팅
1) Docker 설치 (RTX2080TI 서버 및 NIPA 서버)
- 먼저, Docker를 설치한다.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release -y
sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg
sudo echo "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io -y
sudo service docker status
- Docker 버전을 확인한다.
2) Docker Compose 설치 (NIPA 서버)
- Docker Compose를 사용할 수 있는지 확인한다.
- 위와 같이 사용이 불가능하다고 나오면 따로 설치를 해야 한다.
sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.29.2/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
- 바이너리에 실행 권한을 적용한다.
- 설치 후 만약
docker-compose명령이 실패하면 경로를 확인한다. /usr/bin또는 경로의 다른 디렉터리에 대한 심볼릭 링크를 생성할 수도 있다.
- 설치가 완료되었는지 확인한다.
- Redis를 사용할 때 발생하는 Overcommit 에러를 방지하기 위해 다음과 같이
overcommit_memory값을 변경한다.
4. NIPA 서버
- NIPA 서버에서 현재 Docker의 정보를 먼저 확인한다.
Docker Root Dir: /var/lib/docker으로 확인되고, 현재 서버의 디스크 사용량 및 총 용량을 확인한다.- 여기서
df는 "Disk Free"의 약어이며,-h의 "h"는 "Human Readable"의 약어이다.
- 리스트를 확인해서 용량이 넉넉한 디렉터리가 있다면 그 디렉터리로 변경하기 위해 먼저 Docker 데몬을 종료한다.
- 현재 NIPA 서버에서는
/home디렉터리가 넉넉하기 때문에 다음과 같이 작성한다.
- 다시 Docker 데몬을 실행한다.
- 다시 Docker의 정보를 확인하면 바뀌어 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
- 이제, Docker Compose 구성을 위해 새로운 디렉터리를 생성한 후 작업한다.
mkdir ./docker_compose && \
cd ./docker_compose && \
mkdir -p ./proxy ./cache/data ./db/data ./inference ./classifier
- 현재 디렉터리 구조는 다음과 같다.
docker_compose
├── cache
│ └── data
├── classifier
├── db
│ └── data
├── inference
└── proxy
7 directories, 0 files
- 필요한 이미지들을 미리 가져온다.
sudo docker pull nginx && \
sudo docker pull redis && \
sudo docker pull mongo && \
sudo docker pull ubuntu && \
sudo docker pull nvidia/cuda:11.0-base
1) docker-compose.yml 작성
docker-compose.yml를 각 단계에 맞춰서 작성할 것인데, 먼저networks를 구성하고 마지막에 나머지를 작성한다.- 이때 다른 Docker 네트워크와 겹치지 않도록
subnet을 주의해서 설정해야 한다.
./docker-compose.yml
version: "3.8"
networks:
net:
ipam:
driver: default
config:
- subnet: "172.18.1.0/16"
- 현재 디렉터리 및 파일 구조는 다음과 같다.
docker_compose
├── cache
│ └── data
├── classifier
├── db
│ └── data
├── docker-compose.yml
├── inference
└── proxy
7 directories, 1 file
2) Proxy Server
- Proxy Server는
nginx:latest이미지를 이용하고, 현재 버전은 다음과 같다.
nginx이미지를 이용하여 컨테이너를 만들면 웬만한 기본 설정은 다 되어있다.- 그리고 가장 중요한
ulimit의open files값 또한master와worker모두1048576으로 설정되어 있다.
- 설정 파일은 직접 작성한다.
./proxy/nginx.conf
user www-data;
worker_processes 10; # 동시에 Requests 받을 수 있는 수 = worker_processes * worker_connections
pid /run/nginx.pid;
include /etc/nginx/modules-enabled/*.conf;
# worker_rlimit_nofile 2048;
events {
worker_connections 4096; # Reverse Proxy이므로 2배 설정
multi_accept on;
use epoll;
}
http {
##
# Basic Settings
##
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
##
# Upstream Settings
##
upstream application {
server nmt_classifier:8888;
}
##
# Server Settings
##
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://application;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
}
##
# Timeout Settings
##
# keepalive_timeout 86400; # Connection 시간
# keepalive_reqeusts 100 # Connection 횟수
client_body_timeout 86400; # Client로부터 request body를 받는 시간
send_timeout 86400; # Client에게 response body를 보내는 시간
reset_timedout_connection off; # Timeout으로 Connection이 끊긴 경우 리셋
proxy_connect_timeout 86400; # Proxy 서버와 연결되는 시간 (75초를 초과할 수 없음)
proxy_send_timeout 86400; # Proxy 서버에 요청을 보내는 시간
proxy_read_timeout 86400; # Proxy 서버에서 응답을 받는 시간
types_hash_max_size 2048;
# server_tokens off;
# server_names_hash_bucket_size 64;
# server_name_in_redireict off;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
##
# SSL Settings
##
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3; # Dropping SSLv3, ref: POODLE
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
##
# Logging Settings
##
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
##
# Gzip Settings
##
gzip on;
##
# Virtual Host Configs
##
# include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*;
}
- 현재 디렉터리 및 파일 구조는 다음과 같다.
docker_compose
├── cache
│ └── data
├── classifier
├── db
│ └── data
├── docker-compose.yml
├── inference
└── proxy
└── nginx.conf
7 directories, 2 files
3) Cache Server: Data / Count
- Cache Server: Data / Count는
redis:latest이미지를 이용하고, 현재 버전은 다음과 같다.
redis이미지를 이용하여 컨테이너를 만들면 웬만한 기본 설정은 다 되어있다.- 하지만
maxmemory및maxmemory-policy, 그리고 이외의 설정을 조금 수정해야 하기 때문에 설정 파일을 작성한다.
./cache/redis.conf
# Working Directory
dir ./data
# Memory
maxmemory 10g
maxmemory-policy allkeys-lru
# AOF
appendonly yes
appendfsync everysec
# RDB(Snapshot)
save 900 1
save 300 10
save 60 10000
# File Name
appendfilename "appendonly.aof"
dbfilename dump.rdb
# Others
stop-writes-on-bgsave-error no
- 현재 디렉터리 및 파일 구조는 다음과 같다.
docker_compose
├── cache
│ ├── data
│ └── redis.conf
├── classifier
├── db
│ └── data
├── docker-compose.yml
├── inference
└── proxy
└── nginx.conf
7 directories, 3 files
4) DB Server: Data
- DB Server: Data는
mongo:latest이미지를 이용하고, 현재 버전은 다음과 같다.
$ mongo --version
MongoDB shell version v5.0.3
Build Info: {
"version": "5.0.3",
"gitVersion": "657fea5a61a74d7a79df7aff8e4bcf0bc742b748",
"openSSLVersion": "OpenSSL 1.1.1f 31 Mar 2020",
"modules": [],
"allocator": "tcmalloc",
"environment": {
"distmod": "ubuntu2004",
"distarch": "x86_64",
"target_arch": "x86_64"
}
}
- 설정 파일은 건드리지 않는다.
5) Inference Server
- Inference Server는 CUDA를 사용해야 한다.
- 위에서 이미
docker pull로 가져오기는 했지만, 먼저 NIPA 서버의 CUDA 버전부터 확인해야 한다.
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| NVIDIA-SMI 450.102.04 Driver Version: 450.102.04 CUDA Version: 11.0 |
|-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
| | | MIG M. |
|===============================+======================+======================|
| 0 A100-PCIE-40GB On | 00000000:00:06.0 Off | 0 |
| N/A 31C P0 31W / 250W | 0MiB / 40537MiB | 0% Default |
| | | Disabled |
+-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| 1 A100-PCIE-40GB On | 00000000:00:07.0 Off | 0 |
| N/A 31C P0 32W / 250W | 0MiB / 40537MiB | 0% Default |
| | | Disabled |
+-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Processes: |
| GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory |
| ID ID Usage |
|=============================================================================|
| No running processes found |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
- 위에서 이미 가져온
nvidia/cuda:11.0-base이미지를 이용한다.
- Docker에서
nvidia이미지로 컨테이너 생성 시 에러가 발생할 것이다. - 그럼 다음과 같이 Nvidia Repository를 추가한 후
nvidia-container-toolkit을 설치하면 된다.
distribution=$(. /etc/os-release;echo $ID$VERSION_ID) && \
sudo curl -s -L https://nvidia.github.io/nvidia-docker/gpgkey | sudo apt-key add - && \
sudo curl -s -L https://nvidia.github.io/nvidia-docker/$distribution/nvidia-docker.list | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nvidia-docker.list
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install nvidia-container-toolkit -y
sudo systemctl restart docker
- 먼저 Hugging Face로 불러올 모델을 준비해야 한다.
- 하지만 RTX2080TI 서버에서만 NIPA 서버로 데이터를 전송할 수 있다.
- NIPA 서버에서 RTX2080TI 서버에 준비되어 있는 모델을
scp명령어로 가져온다.
- RTX2080TI 서버에서 가져온 모델의 압축을 해제한다.
tar xvfz ./inference/*.tar.gz && \
sudo rm ./inference/*.tar.gz && \
mv ./voiceprint ./inference/voiceprint
- 각 언어마다 사용하는 CUDA를 지정하기 위해서 설정 파일을 작성한다.
./inference/voiceprint/m2m100_418M/setup_config.json
{
"cuda_id": {
"ko": "0",
"en": "0",
"zh-cn": "0",
"zh-tw": "0",
"es": "0",
"fr": "0",
"ru": "0",
"id": "0",
"ja": "1",
"vi": "1",
"de": "1",
"it": "1",
"hi": "1",
"ar": "1",
"pt": "1",
"tl": "1"
}
}
- TorchServe 실행 시 필요한 설정 파일을 작성한다.
./inference/config.properties
# Configure TorchServe listening address and port
inference_address=http://172.18.1.5:9999
management_address=http://172.18.1.5:8081
metrics_address=http://172.18.1.5:8082
# Limit GPU usage
number_of_gpu=0
# Load models at startup
model_store=./model_store
load_models=all
# Other properties
# Worker / Capacity
default_workers_per_model=1
job_queue_size=4096
default_response_timeout=86400
# Models(Override)
models={\
"ko": {\
"1.0": {\
"defaultVersion": true,\
"marName": "ko.mar",\
"minWorkers": 1,\
"maxWorkers": 1,\
"batchSize": 64,\
"maxBatchDelay": 100\
}\
},\
"en": {\
"1.0": {\
"defaultVersion": true,\
"marName": "en.mar",\
"minWorkers": 1,\
"maxWorkers": 1,\
"batchSize": 64,\
"maxBatchDelay": 100\
}\
},\
"zh-cn": {\
"1.0": {\
"defaultVersion": true,\
"marName": "zh-cn.mar",\
"minWorkers": 1,\
"maxWorkers": 1,\
"batchSize": 64,\
"maxBatchDelay": 100\
}\
},\
"zh-tw": {\
"1.0": {\
"defaultVersion": true,\
"marName": "zh-tw.mar",\
"minWorkers": 1,\
"maxWorkers": 1,\
"batchSize": 64,\
"maxBatchDelay": 100\
}\
},\
"es": {\
"1.0": {\
"defaultVersion": true,\
"marName": "es.mar",\
"minWorkers": 1,\
"maxWorkers": 1,\
"batchSize": 64,\
"maxBatchDelay": 100\
}\
},\
"fr": {\
"1.0": {\
"defaultVersion": true,\
"marName": "fr.mar",\
"minWorkers": 1,\
"maxWorkers": 1,\
"batchSize": 64,\
"maxBatchDelay": 100\
}\
},\
"ru": {\
"1.0": {\
"defaultVersion": true,\
"marName": "ru.mar",\
"minWorkers": 1,\
"maxWorkers": 1,\
"batchSize": 64,\
"maxBatchDelay": 100\
}\
},\
"id": {\
"1.0": {\
"defaultVersion": true,\
"marName": "id.mar",\
"minWorkers": 1,\
"maxWorkers": 1,\
"batchSize": 64,\
"maxBatchDelay": 100\
}\
},\
"ja": {\
"1.0": {\
"defaultVersion": true,\
"marName": "ja.mar",\
"minWorkers": 1,\
"maxWorkers": 1,\
"batchSize": 64,\
"maxBatchDelay": 100\
}\
},\
"vi": {\
"1.0": {\
"defaultVersion": true,\
"marName": "vi.mar",\
"minWorkers": 1,\
"maxWorkers": 1,\
"batchSize": 64,\
"maxBatchDelay": 100\
}\
},\
"de": {\
"1.0": {\
"defaultVersion": true,\
"marName": "de.mar",\
"minWorkers": 1,\
"maxWorkers": 1,\
"batchSize": 64,\
"maxBatchDelay": 100\
}\
},\
"it": {\
"1.0": {\
"defaultVersion": true,\
"marName": "it.mar",\
"minWorkers": 1,\
"maxWorkers": 1,\
"batchSize": 64,\
"maxBatchDelay": 100\
}\
},\
"hi": {\
"1.0": {\
"defaultVersion": true,\
"marName": "hi.mar",\
"minWorkers": 1,\
"maxWorkers": 1,\
"batchSize": 64,\
"maxBatchDelay": 100\
}\
},\
"ar": {\
"1.0": {\
"defaultVersion": true,\
"marName": "ar.mar",\
"minWorkers": 1,\
"maxWorkers": 1,\
"batchSize": 64,\
"maxBatchDelay": 100\
}\
},\
"pt": {\
"1.0": {\
"defaultVersion": true,\
"marName": "pt.mar",\
"minWorkers": 1,\
"maxWorkers": 1,\
"batchSize": 64,\
"maxBatchDelay": 100\
}\
},\
"tl": {\
"1.0": {\
"defaultVersion": true,\
"marName": "tl.mar",\
"minWorkers": 1,\
"maxWorkers": 1,\
"batchSize": 64,\
"maxBatchDelay": 100\
}\
}\
}
- MAR 형식의 파일을 생성하기 위해 필요한 핸들러 스크립트 파일도 작성한다.
./inference/handler.py
import ast
import logging
import os
import json
import torch
from abc import ABC
from transformers import M2M100ForConditionalGeneration, AutoTokenizer
from ts.torch_handler.base_handler import BaseHandler
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class InferenceHandler(BaseHandler, ABC):
def __init__(self):
super(InferenceHandler, self).__init__()
self.initialized = False
def initialize(self, ctx):
self.PID = os.getpid()
self.manifest = ctx.manifest
properties = ctx.system_properties
model_dir = properties.get("model_dir")
self.tgt_lang = self.manifest["model"]["modelName"]
setup_config_path = os.path.join(model_dir, "setup_config.json")
with open(setup_config_path) as setup_config_file:
self.setup_config = json.load(setup_config_file)
self.device = "cuda:" + self.setup_config["cuda_id"][self.tgt_lang]
self.model = M2M100ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(model_dir)
self.model.to(self.device)
self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_dir)
logger.info(f"\nPID: {self.PID} / Tgt_Lang: {self.tgt_lang} / Device: {self.device}\nMANIFEST: {self.manifest}\nPROPERTIES: {properties}\n{model_dir} loaded successfully\n")
self.initialized = True
def preprocess(self, requests):
logger.info(f"\nPID: {self.PID} / Tgt_Lang: {self.tgt_lang} / Device: {self.device}\nLength of Requests: {len(requests)}\nRequests: {requests}\n")
input_ids_batch, attention_mask_batch = None, None
input_ids_list, attention_mask_list = [], []
max_length = 0
# requests마다 for문 돌리기
for idx, data in enumerate(requests):
# data 파싱
p = data.get("data")
if p is None:
p = data.get("body")
if isinstance(p, (bytes, bytearray)):
p = ast.literal_eval(p.decode("utf-8"))
src_lang = p["src_lang"]
src_text = p["src_text"]
logger.info(f"\nPID: {self.PID} / Tgt_Lang: {self.tgt_lang} / Device: {self.device}\nSrc_Lang: {src_lang} / Src_Text: {src_text}\n")
# tokenizer src_lang 바꾸기
self.tokenizer.src_lang = "zh" if src_lang == "zh-cn" or src_lang == "zh-tw" else src_lang
# tokenizer에 src_text 넣어서 {"input_ids": Tensor, "attention_mask": Tensor} 만들기
inputs = self.tokenizer(src_text, padding=True, truncation=True, return_tensors='pt')
# input_ids, attention_mask 꺼내기
input_ids = inputs["input_ids"].to(self.device)
attention_mask = inputs["attention_mask"].to(self.device)
# input_ids_list, attention_mask_list에 넣기
input_ids_list.append(input_ids)
attention_mask_list.append(attention_mask)
# requests에 들어온 src_text의 max_length 구하기 -> padding에 쓰기
if input_ids.shape is not None:
if input_ids.shape[1] >= max_length:
max_length = input_ids.shape[1]
# input_ids_list의 index 수만큼 돌리기
for i in range(len(input_ids_list)):
# 현재 index의 length 구하기
length = input_ids_list[i].shape[1]
# (max_length - length)로 padding에 쓸 길이 구하기
pad_length = max_length - length
# pad_ones는 input_ids에 들어가는 pad_token_id
pad_ones = torch.ones(1, pad_length, dtype=torch.long).to(self.device)
# pad_zeros는 attention_mask에 들어가는 pad_token_id
pad_zeros = torch.zeros(1, pad_length, dtype=torch.long).to(self.device)
# padding
input_ids_list[i] = torch.cat((input_ids_list[i], pad_ones), dim=1)
attention_mask_list[i] = torch.cat((attention_mask_list[i], pad_zeros), dim=1)
# input_ids_batch, attention_mask_batch에 넣기
if input_ids.shape is not None:
if input_ids_batch is None:
input_ids_batch = input_ids_list[i]
attention_mask_batch = attention_mask_list[i]
else:
input_ids_batch = torch.cat((input_ids_batch, input_ids_list[i]), dim=0)
attention_mask_batch = torch.cat((attention_mask_batch, attention_mask_list[i]), dim=0)
return (input_ids_batch, attention_mask_batch)
def inference(self, preprocessed):
input_ids_batch, attention_mask_batch = preprocessed
encoded_batch = {"input_ids": input_ids_batch, "attention_mask": attention_mask_batch}
# generate에 {"input_ids": Tensor[[], [], ...], "attention_mask": Tensor[[], [], ...]} 넣고 batch로 돌리기
generated_tokens = self.model.generate(
**encoded_batch,
forced_bos_token_id=self.tokenizer.get_lang_id("zh" if self.tgt_lang == "zh-cn" or self.tgt_lang == "zh-tw" else self.tgt_lang),
num_beams=5,
)
# batch_decode로 generated_tokens를 batch로 돌리기
translated_batch = self.tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True)
logger.info(f"\nPID: {self.PID} / Tgt_Lang: {self.tgt_lang} / Device: {self.device}\nTranslated: {translated_batch}\n")
return translated_batch
def postprocess(self, inferred_batch):
# outputs 형식에 맞게 만들기
postprocessed = [{"tgt_text": tgt_text} for tgt_text in inferred_batch]
return postprocessed
def handle(self, requests, context):
self.context = context
preprocessed = self.preprocess(requests)
inferred_batch = self.inference(preprocessed)
postprocessed = self.postprocess(inferred_batch)
return postprocessed
- 이제 MAR 형식의 파일 생성 및 TorchServe 실행과 관련된 Bash 스크립트를 작성한다.
./inference/torchserve.sh
#!/bin/bash
initialize() {
if [ ! -d ./handlers ]; then mkdir ./handlers; fi
if [[ $(ls ./handlers/ | wc -l) > 0 ]]; then rm ./handlers/*; fi
if [ -d ./logs ]; then rm -rf ./logs; fi
if [ ! -d ./model_store ]; then mkdir ./model_store; fi
if [[ $(ls ./model_store/ | wc -l) > 0 ]]; then rm ./model_store/*; fi
if [ -f ./main_model_dirlist.txt ]; then rm ./main_model_dirlist.txt; fi
if [ -f ./sub_model_dirlist.txt ]; then rm ./sub_model_dirlist.txt; fi
}
create_model_names() {
arr=$2[@]
model_names=("${!arr}")
if [ -f ./$1_model_names.txt ]; then rm ./$1_model_names.txt; fi
for model_name in "${model_names[@]}";
do
echo $model_name >> ./$1_model_names.txt
done
}
create_handlers() {
cat ./$1_model_names.txt | parallel -k cp ./handler.py ./handlers/{}.py
}
create_files() {
echo | ls $2 > ./$1_model_dirlist.txt
readarray files < ./$1_model_dirlist.txt
if [ -f ./$1_model_dirlist.txt ]; then rm ./$1_model_dirlist.txt; fi
for ids in ${!files[@]}
do
if [[ "${files[$ids]}" =~ ".bin" ]]; then
model_file=${files[$ids]}
files_len=$((files_len-1))
else
file_name=${files[$ids]}
extra_files_args=$extra_files_args$2/$file_name,
fi
done
extra_files_args=`echo $extra_files_args | tr -d ' '`
extra_files_args=${extra_files_args%?}
echo "$model_file $extra_files_args"
}
create_mars() {
echo Torch Model Archiver Start - $1...
cat ./$1_model_names.txt | parallel -k time torch-model-archiver --model-name {} --version $2 --serialized-file $3/$4 --handler ./handlers/{}.py --extra-files $5 && \
cat ./$1_model_names.txt | parallel -k mv ./{}.mar ./model_store/{}.mar && \
sleep 1s
if [ -f ./$1_model_names.txt ]; then rm ./$1_model_names.txt; fi
}
main_model_names=("ko" "en" "zh-cn" "zh-tw" "es" "fr" "ru" "id" "ja" "vi" "de" "it" "hi" "ar" "pt" "tl")
sub_model_names=()
main_model_dir=./voiceprint/m2m100_418M
sub_model_dir="sub_model_dir"
model_ver=1.0
initialize
create_model_names "main" main_model_names
if [[ ${#sub_model_names[@]} > 0 ]]; then
create_model_names "sub" sub_model_names
fi
create_handlers "main"
if [[ ${#sub_model_names[@]} > 0 ]]; then
create_handlers "sub"
fi
readarray main_files <<< "$(create_files 'main' $main_model_dir)"
if [[ ${#sub_model_names[@]} > 0 ]]; then
readarray sub_files <<< "$(create_files 'sub' $sub_model_dir)"
fi
create_mars "main" $model_ver $main_model_dir ${main_files[0]} ${main_files[1]}
if [[ ${#sub_model_names[@]} > 0 ]]; then
create_mars "sub" $model_ver $sub_model_dir ${sub_files[0]} ${sub_files[1]}
fi
torchserve --start --ts-config ./config.properties
while true; do echo 'TorchServe Running...'; sleep 1s; done
- Anaconda 환경에서 실행할 것이기 때문에 초기화 파일도 작성한다.
./inference/conda_init.txt
__conda_setup="$('/root/anaconda3/bin/conda' 'shell.bash' 'hook' 2> /dev/null)"
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
eval "$__conda_setup"
else
if [ -f "/root/anaconda3/etc/profile.d/conda.sh" ]; then
. "/root/anaconda3/etc/profile.d/conda.sh"
else
export PATH="/root/anaconda3/bin:$PATH"
fi
fi
unset __conda_setup
- 이제 모델과 다른 설정 파일, Python Dependencies 설치도 고려하여
Dockerfile을 작성한다.
./inference/Dockerfile
FROM nvidia/cuda:11.0-base
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
ENV TZ=Asia/Seoul
ENV PATH /root/anaconda3/bin:$PATH
COPY ./inference/conda_init.txt /inference/conda_init.txt
RUN chsh root -s /bin/bash
RUN apt-get update
RUN apt-get install sudo -y && \
apt-get install vim -y && \
apt-get install htop -y && \
apt-get install curl -y && \
apt-get install wget -y && \
apt-get install tmux -y && \
apt-get install git -y && \
apt-get install tzdata -y && \
apt-get install parallel -y
RUN echo "set encoding=utf-8" >> /etc/vim/vimrc && \
echo "set fileencodings=utf-8,cp949" >> /etc/vim/vimrc
RUN curl -O https://repo.anaconda.com/archive/Anaconda3-2021.05-Linux-x86_64.sh && \
bash Anaconda3-2021.05-Linux-x86_64.sh -b && \
rm Anaconda3-2021.05-Linux-x86_64.sh
WORKDIR /inference
RUN mkdir ./handlers
RUN cat ./conda_init.txt >> ~/.bashrc && \
rm ./conda_init.txt
RUN /bin/bash -c "source ~/.bashrc"
RUN /bin/bash -c "source activate"
RUN conda update conda -y
RUN git clone https://github.com/pytorch/serve.git
RUN mv ./serve/ts_scripts . && \
mv ./serve/requirements . && \
rm -rf ./serve
RUN python ./ts_scripts/install_dependencies.py --cuda=cu111
RUN pip install torchserve torch-model-archiver torch-workflow-archiver sentencepiece
RUN conda install -c huggingface transformers -y
RUN rm -rf ./ts_scripts && \
rm -rf ./requirements
- 현재 디렉터리 및 파일 구조는 다음과 같다.
docker_compose
├── cache
│ ├── data
│ └── redis.conf
├── classifier
├── db
│ └── data
├── docker-compose.yml
├── inference
│ ├── conda_init.txt
│ ├── config.properties
│ ├── Dockerfile
│ ├── handler.py
│ ├── torchserve.sh
│ └── voiceprint
│ └── m2m100_418M
│ ├── config.json
│ ├── pytorch_model.bin
│ ├── sentencepiece.bpe.model
│ ├── setup_config.json
│ ├── special_tokens_map.json
│ ├── tokenizer_config.json
│ └── vocab.json
└── proxy
└── nginx.conf
9 directories, 15 files
6) Classifier Server
- Classifier Server는
ubuntu:latest이미지를 이용하여 구축한다. - 하지만 NIPA 서버의 Classifier Server뿐만 아니라 RTX2080TI 서버의 Client에서도 Anaconda 환경이 필요하기 때문에 중간 지점에서 커밋 후 푸시할 것이다.
ubuntu이미지를 컨테이너로 만들어 실행한다.
- 필요한 툴을 설치한다.
apt-get update && \
apt-get install sudo -y && \
apt-get install vim -y && \
apt-get install htop -y && \
apt-get install curl -y && \
apt-get install wget -y && \
apt-get install tmux -y && \
apt-get install git -y && \
apt-get install tzdata -y
vim인코딩을 설정한다.
echo "set encoding=utf-8" >> /etc/vim/vimrc && \
echo "set fileencodings=utf-8,cp949" >> /etc/vim/vimrc
- Anaconda를 다운로드한 후 설치한다.
curl -O https://repo.anaconda.com/archive/Anaconda3-2021.05-Linux-x86_64.sh && \
bash Anaconda3-2021.05-Linux-x86_64.sh
- 다운로드한 Anaconda 설치용 스크립트를 삭제한다.
- Anaconda 환경변수를 초기화한다.
active environment : base
active env location : /root/anaconda3
shell level : 1
user config file : /root/.condarc
populated config files :
conda version : 4.10.1
conda-build version : 3.21.4
python version : 3.8.8.final.0
virtual packages : __linux=4.15.0=0
__glibc=2.31=0
__unix=0=0
__archspec=1=x86_64
base environment : /root/anaconda3 (writable)
conda av data dir : /root/anaconda3/etc/conda
conda av metadata url : https://repo.anaconda.com/pkgs/main
channel URLs : https://repo.anaconda.com/pkgs/main/linux-64
https://repo.anaconda.com/pkgs/main/noarch
https://repo.anaconda.com/pkgs/r/linux-64
https://repo.anaconda.com/pkgs/r/noarch
package cache : /root/anaconda3/pkgs
/root/.conda/pkgs
envs directories : /root/anaconda3/envs
/root/.conda/envs
platform : linux-64
user-agent : conda/4.10.1 requests/2.25.1 CPython/3.8.8 Linux/4.15.0-72-generic ubuntu/20.04.2 glibc/2.31
UID:GID : 0:0
netrc file : None
offline mode : False
ctrl + p + q로 컨테이너 밖으로 나간 후 다음과 같이 커밋한다.
- 이미지가 커밋되었는지 확인한다.
- Docker에 로그인을 한 후 User Id 변수를 지정하는데, 이때 User Id 변수는 Docker 로그인을 할 때 썼던 계정 이름이다.
- 이미지에 태그를 달아준다.
- 태그가 적용되어 있는 이미지를 Docker Hub에 푸시한다.
- RTX2080TI 서버에서 Client를 구축할 때 지금 푸시한 이미지를 이용하면 된다.
- 이제 다시 Docker Compose에서 Classifier Server를 구성하기 위한 단계로 돌아가는데, 먼저 Python 스크립트부터 작성한다.
- 다음은 FastAPI를 사용할 때의 코드이다.
./classifier/classifier.py
from fastapi import FastAPI, Body, Header, HTTPException, status
from fastapi.responses import JSONResponse
from fastapi.exceptions import RequestValidationError
from fastapi.encoders import jsonable_encoder
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from opencc import OpenCC
import starlette
import logging
import redis
import pymongo
import hashlib
import aiohttp
import json
import os
class Classifier:
def __init__(self):
self.project_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
self.json_name = "api_token.json"
self.json_path = os.path.join(self.project_dir, self.json_name)
self.PID = os.getpid()
logging.info(f"PID: {self.PID} / Loaded Classifier")
if not os.path.isfile(self.json_path):
logging.error(f"PID: {self.PID} / {self.json_path} does not exist!")
self.load()
def load(self):
with open(self.json_path, "r") as json_file:
self.json_data = json.load(json_file)
logging.info(f"PID: {self.PID} / JSON file loaded from {self.json_path}")
class Data(BaseModel):
src_lang: str = Field(..., min_length=2, max_length=5)
src_text: str = Field(..., min_length=1)
tgt_lang: str = Field(..., min_length=2, max_length=5)
app = FastAPI()
logging.basicConfig(filename="./log.log", level=logging.DEBUG)
inference_url = os.environ["INFERENCE_URL"]
@app.on_event("startup")
async def startup_event():
app.session = aiohttp.ClientSession()
app.classifier = Classifier()
app.api_tokens = app.classifier.json_data.values()
app.redis_data = redis.StrictRedis(host="nmt_cache", port=6379, db=0)
app.redis_count = redis.StrictRedis(host="nmt_cache", port=6379, db=1)
app.mongo = pymongo.MongoClient(host="nmt_db", port=27017)["nmt_db"]["nmt_collection"]
app.langs = ["ko", "en", "zh-cn", "zh-tw", "es", "fr", "ru", "id", "ja", "vi", "de", "it", "hi", "ar", "pt", "tl"]
app.cc_t2s = OpenCC("t2s")
app.cc_s2tw = OpenCC("s2tw")
@app.on_event("shutdown")
async def shutdown_event():
await app.session.close()
@app.exception_handler(RequestValidationError)
async def validation_exception_handler(
request: starlette.requests.Request, exc: RequestValidationError
) -> JSONResponse:
logging.info(f"Invalid Body: {str(exc)}")
return JSONResponse({"detail": str(exc)}, status_code=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST)
@app.post("/", status_code=status.HTTP_200_OK)
async def main(*, data: Data = Body(...), authorization=Header(...)) -> JSONResponse:
if authorization not in app.api_tokens:
logging.error(f"{app.classifier.PID}: Invalid API Token - {authorization}")
raise HTTPException(
status_code=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED, detail="Invalid API Token"
)
body = jsonable_encoder(data)
src_lang = body["src_lang"]
src_text = body["src_text"]
tgt_lang = body["tgt_lang"]
if src_lang not in app.langs:
logging.error(f"{app.classifier.PID}: Invalid Src_Lang - {src_lang}")
raise HTTPException(
status_code=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST, detail="Invalid Src_Lang"
)
if tgt_lang not in app.langs:
logging.error(f"{app.classifier.PID}: Invalid Tgt_Lang - {tgt_lang}")
raise HTTPException(
status_code=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST, detail="Invalid Tgt_Lang"
)
h = hashlib.new("sha256")
h.update(src_lang.encode("utf-8"))
h.update(src_text.encode("utf-8"))
h.update(tgt_lang.encode("utf-8"))
hashed_key = h.hexdigest()
check_redis = app.redis_data.get(hashed_key)
if check_redis is not None:
tgt_text = dict(json.loads(check_redis.decode("utf-8")))["tgt_text"]
count = int(app.redis_count.incr(hashed_key, 1))
logging.info(
f"PID: {app.classifier.PID}\n Src_Lang: {src_lang} / Src_Text: {src_text}\n Tgt_Lang: {tgt_lang} / Tgt_Text: {tgt_text}\n Get from Cache - {count} Time(s)"
)
else:
URL = inference_url + tgt_lang
async with app.session.post(URL, json={"src_lang": src_lang, "src_text": app.cc_t2s.convert(src_text) if src_lang == "zh-cn" or src_lang == "zh-tw" else src_text, "tgt_lang": tgt_lang}) as response:
response_data = await response.read()
tgt_text = json.loads(response_data)["tgt_text"]
tgt_text = app.cc_s2tw.convert(tgt_text) if tgt_lang == "zh-tw" else tgt_text
if not tgt_text:
logging.error(f"{app.classifier.PID}: Translation failed")
raise HTTPException(
status_code=status.HTTP_500_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, detail="Translation failed"
)
data_dict = {
"src_lang": src_lang,
"src_text": src_text,
"tgt_lang": tgt_lang,
"tgt_text": tgt_text,
}
dict_value = json.dumps(data_dict, ensure_ascii=False).encode("utf-8")
app.redis_data.set(hashed_key, dict_value)
app.redis_count.set(hashed_key, 0)
app.mongo.insert_one(data_dict)
logging.info(
f"PID: {app.classifier.PID}\n Src_Lang: {src_lang} / Src_Text: {src_text}\n Tgt_Lang: {tgt_lang} / Tgt_Text: {tgt_text}\n Set to Cache/DB"
)
body.update({"tgt_text": tgt_text})
return JSONResponse(content=jsonable_encoder(body))
- 다음은 Flask를 사용할 때의 코드이다.
./classifier/classifier.py
from flask import Flask, request
from opencc import OpenCC
import redis
import pymongo
import hashlib
import requests
import logging
import json
import os
class Classifier:
def __init__(self):
self.project_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
self.json_name = "api_token.json"
self.json_path = os.path.join(self.project_dir, self.json_name)
self.PID = os.getpid()
logging.info(f"PID: {self.PID} / Loaded Classifier!")
if not os.path.isfile(self.json_path):
logging.error(f"PID: {self.PID} / {self.json_path} does not exist!")
self.load()
def load(self):
with open(self.json_path, "r") as json_file:
self.json_data = json.load(json_file)
logging.info(f"PID: {self.PID} / JSON file loaded from {self.json_path}")
def request_text(URL: str, body: dict):
src_lang = body["src_lang"]
src_text = body["src_text"]
tgt_lang = body["tgt_lang"]
response = requests.post(URL, data=json.dumps({"src_lang": src_lang, "src_text": cc_t2s.convert(src_text) if src_lang == "zh-cn" or src_lang == "zh-tw" else src_text, tgt_lang})).json()
return response
app = Flask(__name__)
logging.basicConfig(filename="./log.log", level=logging.DEBUG)
inference_url = os.environ["INFERENCE_URL"]
classifier = Classifier()
api_tokens = classifier.json_data.values()
redis_data = redis.StrictRedis(host="nmt_cache", port=6379, db=0)
redis_count = redis.StrictRedis(host="nmt_cache", port=6379, db=1)
mongo = pymongo.MongoClient(host="nmt_db", port=27017)["nmt_db"]["nmt_collection"]
cc_t2s = OpenCC("t2s")
cc_s2tw = OpenCC("s2tw")
@app.route("/", methods=["POST"])
def main():
headers = request.headers
body = request.get_json(force=True)
if headers["Authorization"] in api_tokens:
src_lang = body["src_lang"]
src_text = body["src_text"]
tgt_lang = body["tgt_lang"]
h = hashlib.new("sha256")
h.update(src_lang.encode("utf-8"))
h.update(src_text.encode("utf-8"))
h.update(tgt_lang.encode("utf-8"))
hashed_key = h.hexdigest()
check_redis = redis_data.get(hashed_key)
if check_redis is not None:
tgt_text = dict(json.loads(check_redis.decode("utf-8")))["tgt_text"]
count = int(redis_count.incr(hashed_key, 1))
logging.info(f"PID: {classifier.PID}\n Src_Lang: {src_lang} / Src_Text: {src_text}\n Tgt_Lang: {tgt_lang} / Tgt_Text: {tgt_text}\n Get from Cache - {count} Times")
else:
URL = inference_url + tgt_lang
tgt_text = request_text(URL, body)["tgt_text"]
tgt_text = cc_s2tw.convert(tgt_text) if tgt_lang == "zh-tw" else tgt_text
data_dict = {
"src_lang": src_lang,
"src_text": src_text,
"tgt_lang": tgt_lang,
"tgt_text": tgt_text
}
dict_value = json.dumps(data_dict, ensure_ascii=False).encode("utf-8")
redis_data.set(hashed_key, dict_value)
redis_count.set(hashed_key, 0)
mongo.insert_one(data_dict)
logging.info(f"PID: {classifier.PID}\n Src_Lang: {src_lang} / Src_Text: {src_Text}\n Tgt_Lang: {tgt_lang} / Tgt_Text: {tgt_text}\n Set to Cache/DB")
body.update({"tgt_text": tgt_text})
return body
else:
logging.error(f"API Token Error!")
return "API Token Error!"
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(host="0.0.0.0", port="80", debug=True)
- API Token을 요구해야 하기 때문에 API Token을 관리할 수 있는 API Token Manager를 작성한다.
./classifier/api_token_manager.py
import os
import json
import random
import bcrypt
class ApiTokenManager:
def __init__(self):
self.project_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
self.json_name = "api_token.json"
self.json_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(self.project_dir, self.json_name))
if not os.path.isfile(self.json_path):
self.json_data = {}
self.save()
self .load()
def save(self):
with open(self.json_path, "w") as json_file:
json.dump(self.json_data, json_file)
print(f"JSON file saved to {self.json_path}")
def load(self):
with open(self.json_path, "r") as json_file:
self.json_data = json.load(json_file)
print(f"JSON file loaded from {self.json_path}")
def generate_token(self, client_name: str):
password = str(random.SystemRandom(7)) + client_name
api_token = bcrypt.hashpw(password.encode("utf-8"), bcrypt.gensalt()).decode("utf-8")
print(f"Client Name {client_name} / API Token {api_token} has generated!")
return api_token
def create(self, client_name: str):
if client_name in self.json_data.keys():
print(f"Client Name {client_name} already exists!")
else:
self.json_data[client_name] = self.generate_token(client_name)
def read(self, option: str):
if option == "all":
print(self.json_data)
else:
if option in self.json_data.keys():
print(self.json_data[option])
else:
print("Enter Valid Client Name!")
def update(self, client_name: str):
if client_name in self.json_data.keys():
option = input("Enter Update Option\n ---> (Name / Token)").lower()
if option == "name":
new_client_name = input("Enter New Client Name\n ---> (STRING)").lower()
if new_client_name in self.json_data.keys():
print(f"Client Name {new_client_name} already exists!")
else:
self.json_data[new_client_name] = self.json_data.pop(client_name)
print(f"Client Name {client_name} has changed to {new_client_name}")
elif option == "token":
self.json_data[client_name] = self.generate_token(client_name)
else:
print("Enter Valid Option!")
else:
print("Enter Valid Client Name!")
def delete(self, client_name: str):
if client_name in self.json_data.keys():
check = input("Delete Client?\n ---> (YES / NO)").lower()
if check == "yes":
del self.json_data[client_name]
print("Client Name {client_name} has been deleted!")
else:
print("Nothing Done")
else:
print("Enter Valid Client Name!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
atm = ApiTokenManager()
while True:
command = input("1. Create (C)\n2. Read (R)\n3. Update (U)\n4. Delete (D)\n5. Save (S)\n6. Init (I)\n7. Exit (E)\n ---> (COMMAND)").lower()
if command == "c":
client_name = input("Enter Client Name\n ---> (STRING)").lower()
atm.create(client_name)
elif command == "r":
option = input("Enter Read Option\n ---> (ALL / Client Name)").lower()
atm.read(option)
elif command == "u":
client_name = input("Enter Client Name\n ---> (STRING)").lower()
atm.update(client_name)
elif command == "d":
client_name = input("Enter Client Name\n ---> (STRING)").lower()
atm.delete(client_name)
elif command == "s":
atm.save()
elif command == "i":
atm.load()
elif command == "e":
print("Bye Bye")
break
else:
print("Enter Valid Command!")
- 그리고 미리 만들어 둔 VoicePrint의 API Token을 생성한다.
./classifier/api_token.json
{ "voiceprint": "$2b$12$sUlMELV0B9Uj.UyvaE5Yq.c6um9hcLqdfWQTy1sNiirVCQZ8sI2ZG" }
- Gunicorn을 사용하기 위한 설정 파일을 작성한다.
- 다음은 FastAPI를 사용할 때의 코드이다.
./classifier/gunicorn.conf.py
import multiprocessing
# Python Module:Variable
wsgi_app = "classifier:app"
# Host:Port
bind = "172.18.1.6:8888"
# Worker Class == Default: "sync"
worker_class = "uvicorn.workers.UvicornWorker"
# Num of Workers
#workers = int(multiprocessing.cpu_count() * 0.1)
workers = 1
# Timeout == 0(Deactivate)
timeout = 0
- 다음은 Flask를 사용할 때의 코드이다.
./classifier/gunicorn.conf.py
import multiprocessing
# Python Module:Variable
wsgi_app = "classifier:app"
# Host:Port
bind = "172.18.1.6:8888"
# Worker Class == Default: "sync"
worker_class = "gevent"
# Num of Workers
# workers = int(multiprocessing.cpu_count() * 0.1)
workers = 1
# Num of Worker Connections
worker_connections = 1024
# Timeout == 0(Deactivate)
timeout = 0
- 이제 다른 설정 파일, Python Dependencies 설치도 고려하여
Dockerfile을 작성한다. - 다음은 FastAPI를 사용할 때의 코드이다.
./classifier/Dockerfile
FROM saemc27/anaconda-dev:1.0
ENV PATH /root/anaconda3/bin:$PATH
RUN /bin/bash -c "source ~/.bashrc"
RUN conda update conda -y
RUN pip install redis pymongo
RUN pip install gunicorn uvicorn[standard] fastapi[all] aiohttp
RUN pip install bcrypt opencc
- 다음은 Flask를 사용할 때의 코드이다.
./classifier/Dockerfile
FROM saemc27/anaconda-dev:1.0
ENV PATH /root/anaconda3/bin:$PATH
RUN /bin/bash -c "source ~/.bashrc"
RUN conda update conda -y
RUN pip install redis pymongo
RUN pip install gunicorn flask gevent
RUN pip install bcrypt requests opencc
- 현재 디렉터리 및 파일 구조는 다음과 같다.
docker_compose
├── cache
│ ├── data
│ └── redis.conf
├── classifier
│ ├── api_token.json
│ ├── api_token_manager.py
│ ├── classifier.py
│ ├── Dockerfile
│ └── gunicorn.conf.py
├── db
│ └── data
├── docker-compose.yml
├── inference
│ ├── conda_init.txt
│ ├── config.properties
│ ├── Dockerfile
│ ├── handler.py
│ ├── torchserve.sh
│ └── voiceprint
│ └── m2m100_418M
│ ├── config.json
│ ├── pytorch_model.bin
│ ├── sentencepiece.bpe.model
│ ├── setup_config.json
│ ├── special_tokens_map.json
│ ├── tokenizer_config.json
│ └── vocab.json
└── proxy
└── nginx.conf
9 directories, 20 files
7) docker-compose.yml 마무리 작성
docker-compose.yml파일을 수정한다.- 이때 Proxy Server만 외부 포트가 필요하므로 나머지는
ports옵션 대신expose옵션으로 설정한다. - 만약
docker-compose.yml파일을 작성하면서 진행할 때 컨테이너가 꺼지지 않도록 하려면entrypoint: [”tail”, “-f”, “/dev/null”]을 설정한다.
./docker-compose.yml
version: "3.8"
services:
nmt_proxy:
container_name: "nmt_proxy"
image: nginx:latest
restart: always
ports:
- "9003:80"
working_dir: /
volumes:
- ./proxy/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
networks:
net:
ipv4_address: 172.18.1.2
nmt_cache:
container_name: "nmt_cache"
image: redis:latest
restart: always
expose:
- "6379"
depends_on:
- nmt_proxy
working_dir: /
volumes:
- ./cache/data:/data
- ./cache/redis.conf:/usr/local/etc/redis/redis.conf
networks:
net:
ipv4_address: 172.18.1.3
entrypoint: ["redis-server", "/usr/local/etc/redis/redis.conf"]
nmt_db:
container_name: "nmt_db"
image: mongo:latest
restart: always
expose:
- "27017"
depends_on:
- nmt_proxy
working_dir: /
volumes:
- ./db/data:/data/db
networks:
net:
ipv4_address: 172.18.1.4
nmt_inference:
container_name: "nmt_inference"
build:
context: .
dockerfile: ./inference/Dockerfile
restart: always
expose:
- "9999"
depends_on:
- nmt_proxy
working_dir: /inference
volumes:
- ./inference/config.properties:/inference/config.properties
- ./inference/handler.py:/inference/handler.py
- ./inference/torchserve.sh:/inference/torchserve.sh
- ./inference/voiceprint:/inference/voiceprint
deploy:
resources:
reservations:
devices:
- capabilities: [gpu]
networks:
net:
ipv4_address: 172.18.1.5
entrypoint: ["/bin/bash", "torchserve.sh"]
nmt_classifier:
container_name: "nmt_classifier"
build:
context: .
dockerfile: ./classifier/Dockerfile
restart: always
expose:
- "8888"
depends_on:
- nmt_proxy
environment:
- INFERENCE_URL=http://172.18.1.5:9999/predictions/
working_dir: /classifier
volumes:
- ./classifier/api_token.json:/classifier/api_token.json
- ./classifier/api_token_manager.py:/classifier/api_token_manager.py
- ./classifier/classifier.py:/classifier/classifier.py
- ./classifier/gunicorn.conf.py:/classifier/gunicorn.conf.py
networks:
net:
ipv4_address: 172.18.1.6
entrypoint: ["gunicorn"]
networks:
net:
ipam:
driver: default
config:
- subnet: "172.18.1.0/16"
8) Docker Compose 실행하기
docker-compose파일을 다 작성했으면 이제 실행한다.
- Docker Compose는 다음과 같이 중단할 수 있다.
- 또한, 다음과 같이 해당 컨테이너의 네트워크를 확인할 수 있다.
- 또는 Docker의 모든 네트워크를 확인할 수도 있다.
- Docker Compose로 구성한 네트워크를 삭제하려면 다음과 같이 해결할 수 있다.
5. RTX2080TI 서버
saemc27/anaconda-dev:1.0이미지로 컨테이너를 다시 만들어서 구축 작업을 진행하는데, 먼저 이미지를 가져온다.
9003번 포트로 지정하여 컨테이너를 생성한다.
- Python Dependencies를 설치한다.
$(base) conda update conda -y && \
conda install pytorch torchvision torchaudio torchtext cpuonly -c pytorch -y && \
pip install streamlit
- Streamlit 코드를 작성한다.
./NMT.py
import json, time
import requests
import streamlit as st
import pandas as pd
from multiprocessing import Process, Queue
from torchtext.data import get_tokenizer
from torchtext.data.metrics import bleu_score
def request_text(idx: int, GMT: str, URL: str, API_TOKEN: str, src_lang: str, src_text: str, tgt_lang: str, result_queue: Queue):
headers = {"Authorization": API_TOKEN}
body = {"src_lang": src_lang, "src_text": src_text, "tgt_lang": tgt_lang}
response = requests.post(URL, data=json.dumps(body), headers=headers)
tgt_text = response.json()["tgt_text"]
print(f"\nIndex: {idx} / GMT: {GMT}\nSrc_Lang: {src_lang} / Src_Text: {src_text}\nTgt_Lang: {tgt_lang} / Tgt_Text: {tgt_text}\n")
result_queue.put((idx, tgt_text))
def main():
# st.set_page_config(layout="wide")
URL = "http://14.49.45.62:9003"
API_TOKEN = "$2b$12$sUlMELV0B9Uj.UyvaE5Yq.c6um9hcLqdfWQTy1sNiirVCQZ8sI2ZG"
lang_codes = {
"Korean": "ko",
"English": "en",
"Chinese-CN": "zh-cn",
"Chinese-TW": "zh-tw",
"Spanish": "es",
"French": "fr",
"Rusian": "ru",
"Indonesian": "id",
"Japanese": "ja",
"Vietnamese": "vi",
"German": "de",
"Italian": "it",
"Hindi": "hi",
"Arabic": "ar",
"Portuguese": "pt",
"Tagalog": "tl"
}
st.title("Many to Many Translator")
language_option = st.selectbox("Choose a Source Language", list(lang_codes.keys()))
if language_option:
src_text = st.text_area(
"Enter text", value="", height=None, max_chars=None, key=None
)
ref_text = ""
if language_option == "Korean" or language_option == "English":
bleu_button = st.checkbox("Check BLEU Score")
if bleu_button:
ref_text = st.text_area("Enter reference:", value="", height=None, max_chars=None, key=None)
col1, col2, col3, col4, col5 = st.columns(5)
if col5.button("Translate text"):
if src_text == "":
st.write("Please enter text for tanslation")
else:
with st.spinner("Running translation..."):
start = time.time()
src_lang = lang_codes.pop(language_option)
GMT = time.ctime(time.time())
print(f"GMT: {GMT}\nSource Language: {language_option}\n")
result_queue = Queue()
idx_list, translated_list, bleu_list = [], [], []
procs = []
procs = [Process(target=request_text, args=(idx, GMT, URL, API_TOKEN, src_lang, src_text, lang_code, result_queue)) for idx, (lang, lang_code) in enumerate(lang_codes.items())]
for proc in procs:
proc.start()
for proc in procs:
proc.join()
while not result_queue.empty():
idx, translated = result_queue.get()
idx_list.append(idx)
translated_list.append(translated)
translated_list = list(pd.DataFrame({"idx": idx_list, "Translated": translated_list}).sort_values(by=["idx"], axis=0)["Translated"])
if len(ref_text) > 0:
tokenizer = get_tokenizer("basic_english")
reference_corpus = [[tokenizer(ref_text)]]
translated_corpus = [tokenizer(translated_list[0])]
bleu_list.append(str(bleu_score(translated_corpus, reference_corpus, max_n=1, weights=[1.0])))
for _ in range(len(lang_codes.keys()) - 1):
bleu_list.append("")
print(translated_list)
df = pd.DataFrame({"Language": list(lang_codes.keys()), "Translated Text": translated_list, "BLEU Score": bleu_list})
else:
print(translated_list)
df = pd.DataFrame({"Language": list(lang_codes.keys()), "Translated Text": translated_list})
st.table(df)
end = time.time()
col1, col2, col3, col4, col5 = st.columns(5)
col5.write(f"{end - start:.5f} sec.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
- Streamlit 코드를 실행한다.
You can now view your Streamlit app in your browser.
Network URL: http://172.17.0.3:9003
External URL: http://14.138.218.153:9003